My 2026 LangChain + Gemini RAG Stack in TypeScript
January 19, 2026
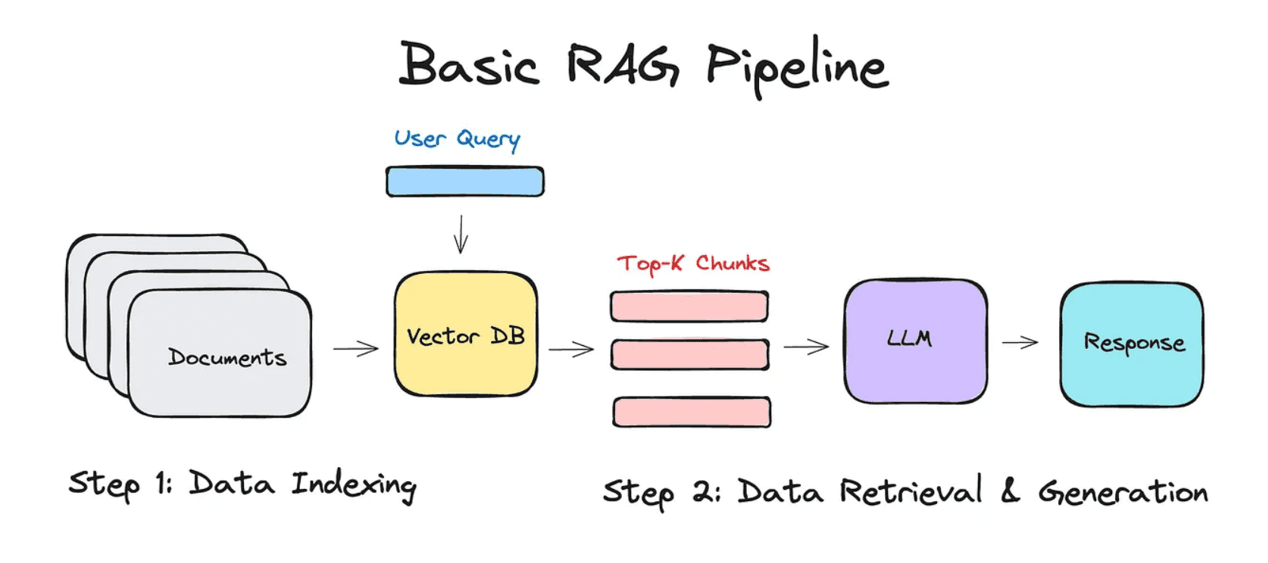
I wanted a RAG system that doesn’t feel like the GenAI MVPs of 2023. It had to be fast on the edge, safe for production, and wired directly into the rest of my portfolio stack. Here’s the playbook I’m using in 2026.
1. Define the Retrieval Contract First
Before touching code, I lock the interface. Every answer is traced, citations are mandatory, and the client receives a latency budget.
export type RAGAnswer = {
answer: string;
citations: Array<{ title: string; url: string; relevance: number }>;
latencyMs: number;
};This contract sits in a shared types/ai.ts module so the Next.js app, the cron workers, and the analytics dashboards stay in sync.
2. Build a Chunking Pipeline with LangChain.js
LangChain’s RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter is still my go-to.
import { RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter } from "langchain/text_splitter";
export const splitDocs = async (rawDocs: string[]) => {
const splitter = new RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter({
chunkSize: 900,
chunkOverlap: 120,
});
return splitter.createDocuments(rawDocs);
};Any asset—Notion export, MDX, or PDF—gets normalized into raw strings before chunking. I collect source metadata so I can cite later.
3. Embed with Gemini 2.0 Flash
Google finally gave us TypeScript SDK parity. I keep embeddings in a dedicated job so rate limits never block user queries.
import { GoogleGenerativeAIEmbeddings } from "@langchain/google";
const embeddings = new GoogleGenerativeAIEmbeddings({
model: "models/embedding-001",
apiKey: process.env.GEMINI_API_KEY!,
});
export const vectorizeDocs = async (docs: Document[]) =>
Promise.all(docs.map((doc) => embeddings.embedQuery(doc.pageContent)));4. Persist to Supabase Vector
I’m still obsessed with Postgres. Supabase’s vector extension lets me stay in SQL land.
import { createClient } from "@supabase/supabase-js";
const supabase = createClient(
process.env.SUPABASE_URL!,
process.env.SUPABASE_SERVICE_ROLE_KEY!,
);
export const storeVectors = async (vectors: number[][], docs: Document[]) => {
const payload = vectors.map((embedding, idx) => ({
embedding,
content: docs[idx].pageContent,
metadata: docs[idx].metadata,
}));
await supabase.from("rag_chunks").insert(payload);
};5. Edge Retrieval with Hybrid Search
Queries live on a Vercel Edge Function. I do hybrid scoring: semantic cosine similarity + keyword BM25 fallback.
export const retrieve = async (query: string) => {
const { data } = await supabase.rpc("hybrid_match", {
query_text: query,
match_threshold: 0.75,
match_count: 6,
});
return data ?? [];
};The RPC wraps pgvector and tsvector in one stored procedure. Game changer.
6. Orchestrate with LangChain RunnableSequence
Responses are small agentic chains.
import { RunnableSequence } from "langchain/schema";
import { ChatGoogleGenerativeAI } from "@langchain/google";
const llm = new ChatGoogleGenerativeAI({
modelName: "gemini-2.0-pro",
apiKey: process.env.GEMINI_API_KEY!,
temperature: 0.2,
});
export const answerQuestion = RunnableSequence.from([
retrieve,
async (chunks, { question }) => ({ question, context: chunks }),
llm.bind({
additionalInstructions:
"Cite every statement with the provided metadata. Return markdown.",
}),
]);7. Trace Everything with LangSmith + OpenTelemetry
Every call pumps into LangSmith and Grafana. If latency spikes, the edge function flips a feature flag and drops to a cached answer stored in Upstash Redis.
8. Frontend Polish
The Next.js route handler simply calls answerQuestion.invoke({ question }) and streams the markdown via ReadableStream. The React side renders citations with hover previews and logs feedback to Supabase.
Need the template? It’s on the private repo. Ping me or drop your email on xaid.in/contact and I’ll share the invite-only launch list.